MySQL vs. MariaDB: Who Dominates the Database Race?
The database is one of the key components of any web application because it contains all the important site data and information in it. Developers spend hours to build the structure and test the performance of the database, to ensure that the execution is smooth and working without any errors. That is why they remain concerned regarding the choice of the right database for the applications, as there are many different database technologies available in the market to choose from.
Comparing MySQL vs MariaDB is one of the most hottest trends in the dev world, as both of these technologies are quite popular databases in the market. Both MySQL and MariaDB are used widely in web applications, offering a range of queries & attributes to sort the tables and schemas in the database.
In this article, I will provide a brief overview of both of these database technologies, their comparison in features, compatibility and more. Let’s first study the inception of MySQL and MariaDB, and what they offer in detail:
A Little About MySQL
MySQL is one of the most used database systems in web applications. It was first introduced in 1995 by a Swedish company named MySQL AB. The company was founded by Michael Monty Widenius, who is originally known as the root creator of MySQL. He was the first person who came up with the idea of open-source database systems so that its community can become large and can later contribute to its advancements.
In 2008, MySQL was first acquired by Sun Microsystems – a renowned tech brand that explored various areas of computational advancements in the IT industry. However, in 2010, the industry’s fastest emerging name and today’s giant Oracle took over Sun Microsystems and its subfields including MySQL. Since then, Oracle took the supervision of MySQL, in fact, rolled out its database built on the same SQL roots named as Oracle Database.
The most significant aspect about MySQL is that it comes up with a GNU General Public License (GPL), which effectively makes its usage applicable for the entire community. It is supported by major operating systems including Linux, UNIX, MacOS, Windows and others.
The database system is part of the LAMP development stack, which is a common term used for a group of major software components. Its acronym can be defined as:
- Linux
- Apache Web Server
- MySQL
- PHP/Perl/Python
The usage of MySQL in PHPMyAdmin highlights its importance for PHP applications. It is the first database made for PHP applications, and was later followed by other databases like MariaDB, PostgreSQL, etc. for specialized usage in different fields.
What is MariaDB?
When Oracle took over Sun Microsystems, a conflict of interest started to develop in between various core engineers of MySQL. They feared that Oracle would alter the state of original MySQL according to their own desired database system. Few changes in the core queries also strengthened this concern, which is why some of them, at last, decided to part their ways with Oracle. That was the point where the inception of MariaDB took place.
The MySQL-forked database system – MariaDB came out first in the market in 2009, introduced from the same MySQL founder Michael Widenius. It can be said as an advanced version of MySQL, as it carries various optimized features of existing SQL. It includes support for JSON APIs, replication of parallel data, various storage engines like Aria, ColumnStore, InnoDB, Cassandra, and others.
It is owned by MariaDB Corporation, which provides training, migration services, remote database management and various other specialized features to its subscribers. It is unarguably one of the fastest increasing database systems in the market, having clientele ranging from Nokia to Teleplan and more.
MySQL vs MariaDB: Key Comparisons
Here are some of the key differences between MySQL and MariaDB database systems:
Database Structure
MySQL is classified as a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS). It works with all the conventional properties of a relational database, i.e. building tables, constraints, views, etc. It uses core database processes to perform various functional operations, such as stored procedures, triggers, roles, and others. To interact with database tables, it uses primary and foreign keys to refer to each other and manage given records precisely.
While MariaDB as said above, is a forked version of MySQL database, containing all the relational properties preconfigured in it. It uses the same database structure and indexes as of MySQL and works quite similarly as well. The good thing about this resemblance is that, when you switch your application to MariaDB, it is by default compatible with it and you won’t have to perform any additional configuration to make things work in a new database.
Database Deployment
MySQL is developed using two languages i.e. C and C++. It is a lightweight database and works with almost all operating systems. It has its binaries available for Linux, Microsoft Windows, OS X, AIX, FreeBSD, HP-UX, BSDi, Novell Netware, NetBSD and many more.
To download MySQL, head over to its installation page, which also includes pre-written guides for installing the database in Microsoft Windows, Linux and OS X.
MariaDB is written in C, C++, Bash & Perl languages, which is why it is considered a bit more advanced as compared to MySQL. It has the installation binaries available for Microsoft Windows, Linux, OS X, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris, and others.
To install MariaDB, you need to first uninstall MySQL from your system, as it is a drop-in replacement of MariaDB. And after uninstalling MySQL, also keep in mind to run the mysql_upgrade command, so that the core files of the system can be upgraded to the new MariaDB version.
Data Replication
Replication is a process that enables database administrators to copy data/records from one database to another. It is a process in which one database acts as a ‘Master’ and the other one as ‘Slave’. Using that identification, administrators can easily replicate data between the desired databases.
MySQL offers asynchronous replication, which means it is a one-way process. It authorizes ‘Master’ databases to copy the data to ‘Slave’ databases, replicating all the tables and attributes at once.
MariaDB, on the other hand, has a similar process with a small tweak. It not only allows ‘Master’ to ‘Slave’ data transfer but also allows ‘Master’ to ‘Master’ replication. This provides administrators a bit of added functionality to work with multiple Master databases at once, allowing them to initiate fast data transfers with enhanced Master authority
Database Clustering
MySQL uses a specialized clustering technology called MySQL Cluster, which provides shared-nothing clustering and auto-sharding for respective databases. It allows administrators to write data to different nodes through a two-phase commit mechanism, to ensure that there isn’t only one point of failure or dependence on a single node.
Whereas, MariaDB uses the Galera Cluster to perform advanced replication for multi-master nodes. It can be easily enabled in MariaDB by just activating the configuration parameters.
Indexes
Both MySQL and MariaDB store indexes (PRIMARY KEY, UNIQUE, INDEX, and FULLTEXT) in B-trees. They also have some exceptions in indexes, which are spatial data types and are stored in R-trees.
Other than these conventional indexes, MySQL also supports hash indexes and uses the InnoDB engine to store the inverted list of FULLTEXT indexes.
Technical Support
As part of Oracle’s Lifetime Support Program, MySQL provides 24/7/365 support to its valued users. Their support team includes expert MySQL developers who are well-versed with all the core features of the platform, and are available round the clock to resolve any major/minor database issue.
Moreover, to facilitate its users, Oracle also offers MySQL Premier Support, Extended Support, and Sustaining Support depending upon the requirements of the project.
On the other hand MariaDB offers a top-skilled support team of engineers who are proficient in both MySQL and MariaDB databases. They also provide 24/7/365 support with a specialized enterprise subscription for mission-critical projects.
How Cloudways Gives You Ease To Manage Databases
Cloudways provides latest MariaDB versions on all its newly launched servers. To select your desired MariaDB version, just navigate to the Settings & Packages tab and choose your desired MariaDB version with a single click drop down.
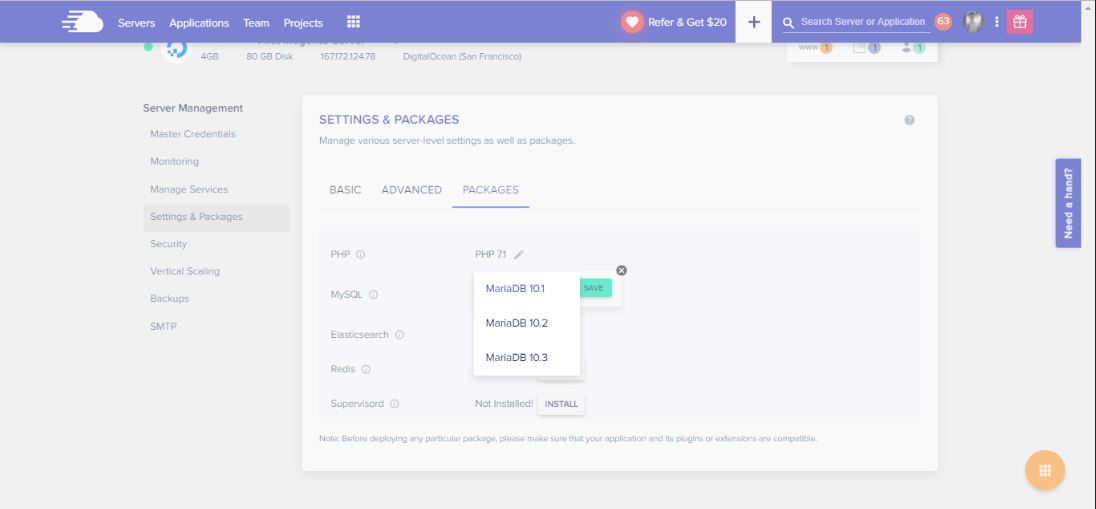
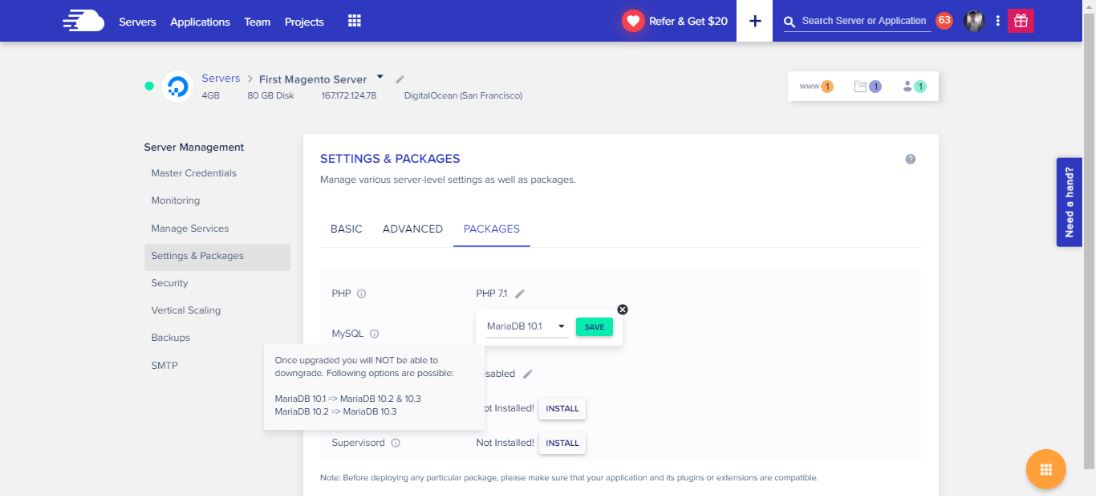
There are multiple MariaDB versions available on the platform including MariaDB 10.1, 10.2 and 10.3. You can select your favorite MariaDB version based on your project requirements. However, keep in mind that once upgraded to the higher version, you cannot downgrade it again to the lower one. Here is the image below which describes the upgrade and downgrade criterias.
Meanwhile, if you want to know some handy tips on how to optimize your database systems to enhance application performance, head over to this MySQL optimization guide to learn some useful performance tips.
Final Words
This brings us to the end of this article which highlighted some of the core differences between MySQL and MariaDB database systems. According to the general dev reviews, MariaDB stands tall as a more powerful database as compared to MySQL. Because it provides several advanced features which are till now not introduced by MySQL, and are neither supported in its compatible apps. Dev-friendly storage engines like XtraDB, Aria and others give MariaDB an edge over MySQL, making it a more lucrative choice for building databases with enhanced functionalities.
If you still have some more questions or want to add your thoughts to this MySQL vs MariaDB comparison, please feel free to write down your suggestions below in the comments section.

Comments
Post a Comment